Health is one of the most important things in life. Yet figures show that in 2019, one in two adults did not know they had diabetes. This justifies the sudden rise in the number of cases recorded. In fact, in 2020, there will be 463 million adults with the disease, compared to only 422 million in 2014.
Before determining how a subject can know if he or she is affected or not, it is reasonable to describe this disease first. How does it manifest itself, and is it transmitted? When is a medical examination necessary? So, without further ado, let’s dive into this blog and learn some of the things to know about diabetes.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is not a disease in itself but rather a state of permanent hyperglycemia in a person. The Egyptians already noticed it at the time of Pharaoh Amenhotep III in the 15th century BC. The patients were in a state of permanent thirst. It is the Greek doctors who gave this name. The word comes from the radical “diabaïno” which means to cross. The subjects were always thirsty, yet they urinated right after drinking.
It was as if the water was flowing through them, but they were not getting anything out of it. Praxagoras of Cos (384-322 BC), a disciple of Socrates, first made the connection with sugar. The Latin word “Mellitus” (from diabetes mellitus) means sweet as honey, hence the term diabetes mellitus or hyperglycemia.
What causes it?
This disease is hereditary. It is transmitted from one generation to another. There is a 5% risk of transmission if only one parent is a carrier as opposed to 30 to 4% if they are both carriers. There are two types of diabetes. The first one, called type 1 or insulin-dependent diabetes (IDD), affects 10% of the subjects and is mostly found in young people. NIDDM (Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes) or fatty diabetes is the second type.
It is common in overweight people and the elderly (mature diabetes). The pancreas does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates the absorption of glucose by the cells. This causes a rise in blood sugar levels and damages certain vital organs such as the kidneys, eyes, and heart. It also leads to the malfunctioning of the nerves and blood vessels. This puts people at risk for stroke.
What are its symptoms?
Polydipsia (intense thirst) and polyuria (excess urine) are the first signs. The subject urinates as soon as he or she drinks a little water. Normal people urinate a lot because they drink a lot. But for them, it is rather the opposite. This causes a perpetual feeling of dry mouth.
Chronic weight loss is also noticed in these people despite an insatiable hunger. To this can be added a progressive blurring of vision. Fatigue and drowsiness are also factors indicating a blood sugar disorder. The patient may also experience cramps in the calves and pain in the feet.
How to detect it and when to test it?
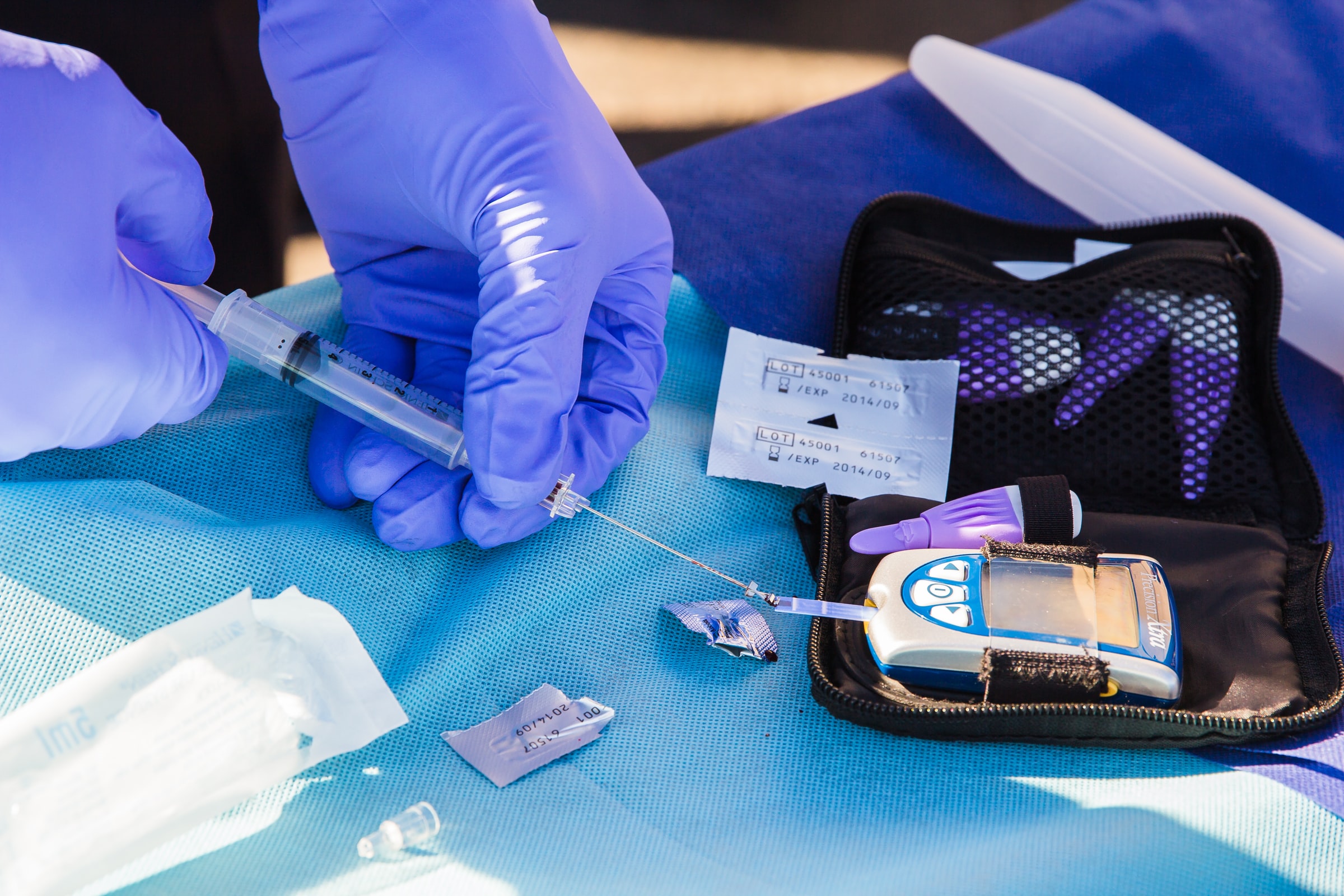
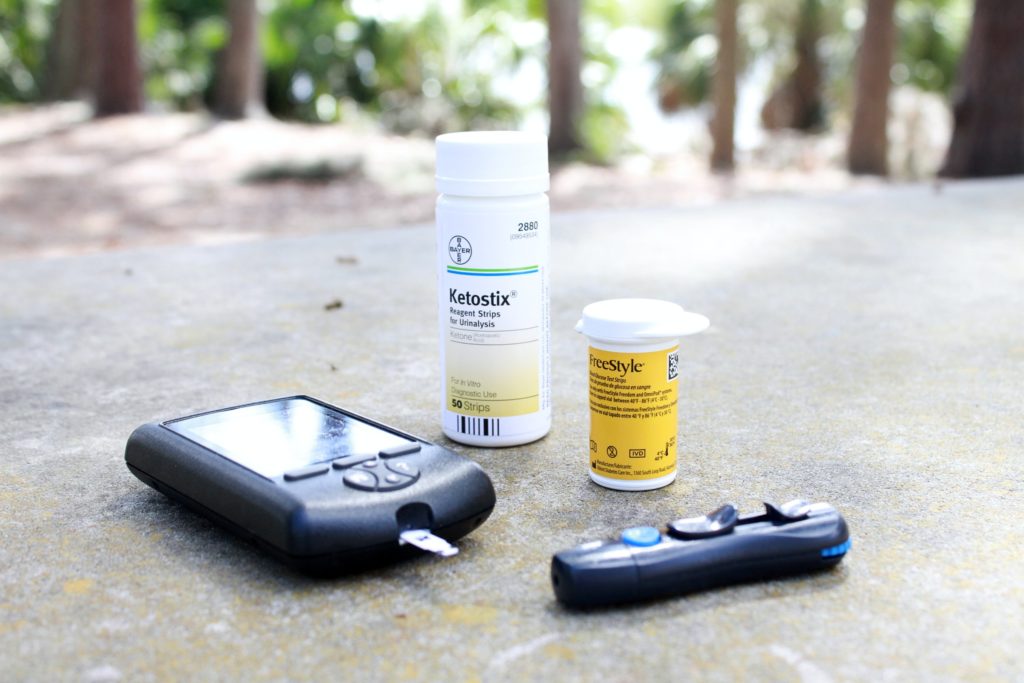
A blood test is the only way to confirm a patient’s diabetic status. This test is performed on a subject who has already fasted for 8 hours. After a small prick on the tip of a finger, it is massaged to obtain a drop of blood which is then placed on a strip. A few seconds later, the meter will display the blood sugar level. The result is positive if the test shows a minimum of 126 mg twice. However, a doctor’s opinion is required to confirm the diagnosis.
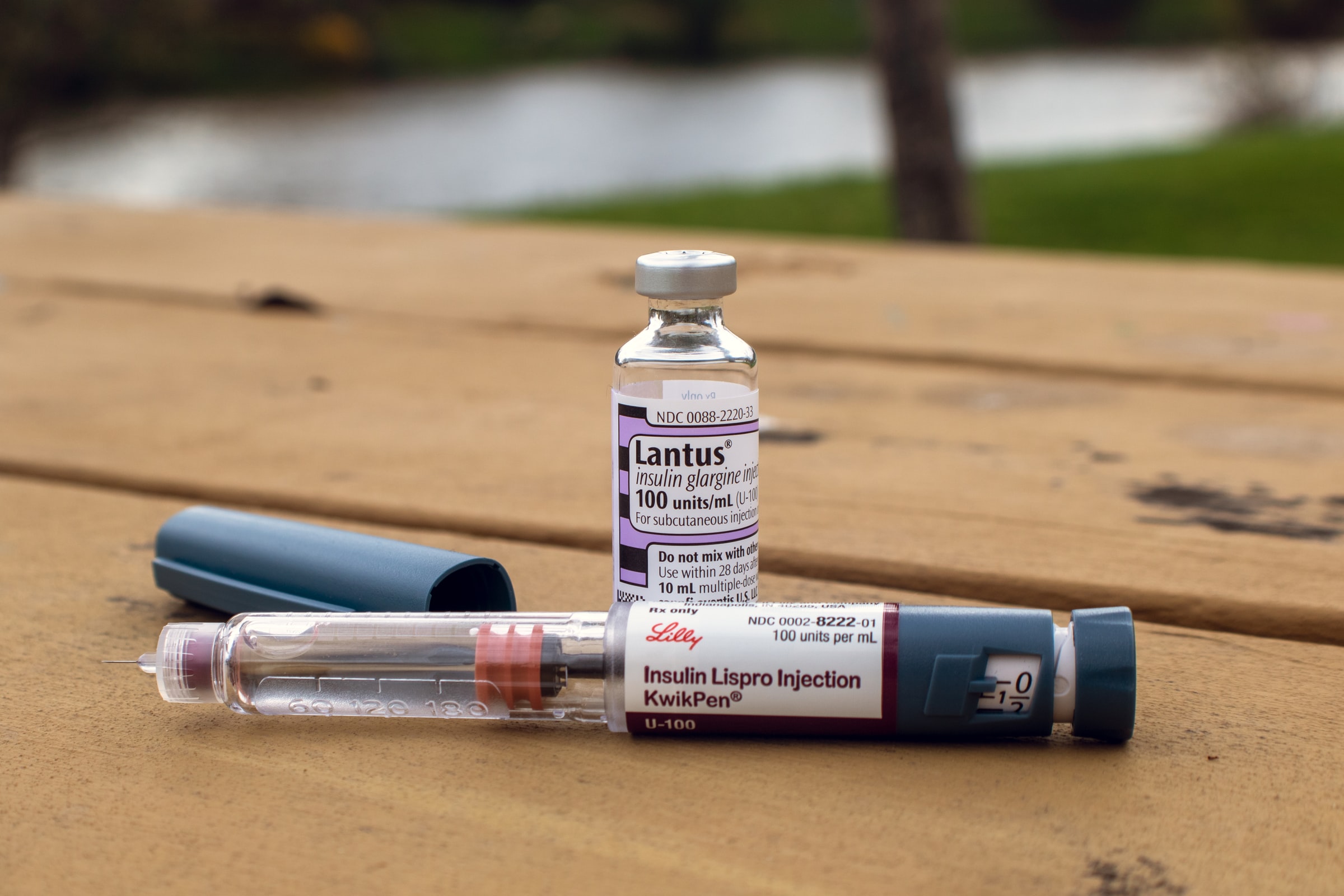
Screenings are recommended if any of the above symptoms persist for 5 to 6 months. In a woman, it is suggested to do the test in the absence of menstruation for 24 to 28 weeks. It will be easier to manage diabetes. It is treated by administering insulin orally or by injection. Nevertheless, living with diabetes requires a healthy diet avoiding foods rich in carbohydrates.
Sound off in the comments section below and tell us what you want to read next and if you want to read more about diabetes.